Gut Health and Digestive health, Why so important?
As a nutritionist and naturopath for gut health, I firmly believe that good gut health is a  foundation for overall health and well-being.
foundation for overall health and well-being.
The digestive system is critical in maintaining the body’s natural balance, supporting the immune system, and promoting overall vitality.
My name is Leah and I have had a funny tummy since childhood. You can benefit from my years of experience.
What is the importance of healthy gut and digestive health and how can it impact our overall health?
The digestive system is responsible for breaking down food and absorbing nutrients into the body.
It is also home to trillions of microorganisms, collectively known as the gut microbiome.
These microorganisms play a critical role in maintaining our overall health, including supporting our immune system, regulating metabolism, and synthesising essential vitamins and minerals.
When the digestive system is not functioning correctly, it can lead to a wide range of gut health problems, including indigestion, bloating, constipation, diarrhea, and even more severe conditions like coeliac disease, and irritable bowel syndrome.
Here is a list of gut-related issues that Leah may be able to help with:
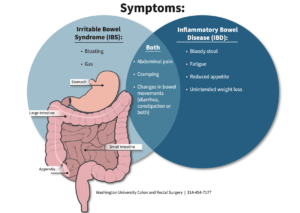
Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS):
- Characterised by abdominal pain, bloating, and changes in bowel habits.
Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD):
- Conditions like Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis involve chronic inflammation of the digestive tract.
What’s the difference between IBD and IBS?
Diverticular Disease
Read more about diverticular disease.
Leaky Gut Syndrome:
- A controversial term referring to increased intestinal permeability that may contribute to various health issues.
Read more about Leaky Gut Syndrome
Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD):
- Chronic acid reflux that can lead to heartburn and other complications.
Read more about GERD
Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth (SIBO):
- Excessive bacterial growth in the small intestine, causing various digestive symptoms.
Constipation and Diarrhea:
- Chronic issues with bowel movements that can impact overall gut health.
Read more about constipation and diarrhea
Food Sensitivities:
- Identifying and addressing sensitivities to certain foods that may contribute to digestive problems.
Read more:
Food Sensitivities Testing
Candida Overgrowth:
- An overgrowth of the Candida fungus in the digestive system, potentially leading to various symptoms.
Read more about Candida Overgrowth
Gallbladder Issues:
- Addressing imbalances or dysfunction in the gallbladder that can affect digestion.
Read more about Gallbladder dysfunction
Gut Dysbiosis:
- Imbalances in the microbial community in the gut, potentially leading to various health problems.
Read more about how to reduce bloating
Functional Gut Disorders:
- Naturopaths may address various functional gastrointestinal disorders that impact digestion and bowel function.
Nutrient Absorption Issues:
- Helping improve the absorption of nutrients from the digestive system.
Read more about how a nutritionist can help nutrient absorption.
Digestive Enzyme Deficiencies:
- Supporting the body in producing and utilizing digestive enzymes effectively.
Read more about how digestive enzymes help your body.
Coeliac Disease:
- A gluten-related autoimmune disorder that affects the small intestine.
Read more about what Ceoliac disease is.
Gut-Brain Axis Issues:
- Addressing the connection between the gut and the brain in conditions like anxiety and depression.
Read more about how the gut affects mental health.
Weight loss
Gut "Second Brain"?
The gut is often referred to as the “second brain,” and for good reason.
There is a powerful connection between gut health and mental health. The gut contains millions of nerve cells that communicate with the brain, and the health of the gut can have a significant impact on mental and emotional well-being.
The Gut-Brain Connection
The gut and the brain are intimately connected, and research suggests that imbalances in the gut can have a significant impact on mental health.
This connection is known as the gut-brain axis.
The gut-brain axis refers to the communication network between the gut and the brain, which is made up of the nervous system, immune system, and endocrine system.
The gut microbiome, which is made up of trillions of microorganisms that live in the digestive tract, plays a crucial role in this connection.
When the gut is healthy, the gut microbiome is in balance, with a diverse range of beneficial bacteria that help to promote healthy digestion and nutrient absorption.
These beneficial bacteria also play a role in regulating the immune system, which can help to reduce inflammation throughout the body, including in the brain.
However, when the gut is imbalanced, with an overgrowth of harmful bacteria, yeast, or other pathogens, this can lead to a disruption in the gut-brain axis, which can contribute to mental health issues.
The Link Between Gut and Mental Health
Research has shown that imbalances in the gut microbiome are associated with a range of mental health conditions, including anxiety, depression, and ADHD.
For example, studies have found that people with depression and anxiety often have an imbalanced gut microbiome, with a lower diversity of beneficial bacteria and an overgrowth of harmful bacteria.
Additionally, research has shown that supplementing with probiotics, or beneficial bacteria, can help to improve symptoms of depression and anxiety.
One reason for this link may be due to the production of neurotransmitters, which are chemicals that communicate messages between nerve cells.
The gut is responsible for producing many of the same neurotransmitters that are found in the brain, including serotonin, which is often called the “feel-good” hormone.
In fact, over 90% of serotonin is produced in the gut. When the gut is imbalanced, this can lead to a disruption in the production of these neurotransmitters, which can contribute to mental health issues.
The intricate link between iron deficiency and gut health is a crucial aspect often overlooked in our well-being.
The gut plays a pivotal role in absorbing and assimilating iron from the foods we consume.
An imbalance in gut health can lead to impaired iron absorption, contributing to deficiencies.
To delve deeper into this connection and explore actionable insights, check out our comprehensive blog on ‘The Gut Connection:Iron and Digestive Health“
Learn more about how optimising gut health can positively impact your iron levels and overall vitality.
How to improve your Gut Health?
These are general suggestions. For some people, these suggestions will make things worse. Please make an appointment to see me or your preferred naturopath or nutritionist before making any major changes to your diet or lifestyle.
I am often asked about the best ways for improving gut health.
The truth is, there are many different factors that can affect the health of your gut, including your diet, lifestyle habits, and overall health.
However, there are some key strategies that you can use to improve your gut health and maintain optimal digestion and nutrient absorption.
Here are some tips to help you get started:
- Eat a variety of fibre-rich foods
Fibre is essential for healthy digestion and a healthy gut. It helps to keep your digestive system moving smoothly and can also help to feed the beneficial bacteria in your gut to promote a healthy gut microbiome and support optimal mental health.
Aim to include a variety of fibre-rich foods in your diet, including fruits, vegetables, whole grains, legumes, nuts and seeds. Try to eat a minimum of 25 grams of fibre per day.
2. Eat bitter foods. For a detailed explanation of the benefits of bitter food on your digestive system click here.
3. Choose fermented foods
Fermented foods are rich in beneficial bacteria, or probiotics, which can help to improve gut health.
Some examples of fermented foods include yogurt, kefir, kimchi, sauerkraut, and miso. Incorporate these foods into your diet regularly to support a healthy gut.
4. Stay hydrated
Drinking enough water is important for overall health, including gut health.
Water helps to keep your digestive system functioning properly and can also help to prevent constipation.
Aim to drink at least 8 cups of water per day.
5. Limit processed foods and sugar
Processed foods and sugar can disrupt the balance of bacteria in your gut and promote the growth of harmful bacteria.
Limit your intake of these foods and instead focus on whole, nutrient-dense foods.
6. Manage stress
Stress can hurt gut health. When stressed, your body releases hormones that can affect digestion and nutrient absorption. Managing stress also balances the gut – brain connection.
Try to manage your stress levels through light exercises or deep breathing exercises.
7. Consider probiotic supplements
If you’re not able to get enough probiotics from your diet, consider taking a probiotic supplement.
Leah can prescribe you a high-quality supplement that contains a variety of different strains of beneficial bacteria that suit your particular needs.
8. Get regular exercise
Regular exercise can help to promote healthy digestion and may also help to reduce inflammation in the gut.
Aim to get at least 30 minutes of moderate exercise per day.
See blog 15 ways to reduce bloating
Improving your gut health is a process that takes time and effort. By incorporating these strategies into your daily routine, you can support a healthy gut and improve your overall health and well-being.
Remember to consult with Leah or your preferred naturopath or nutritionist for gut health if you have any questions or concerns about your gut health or dietary needs.