The Impact of Alcohol on Gut Health: What You Need to Know
Alcohol is a ubiquitous part of social culture, often associated with celebrations, relaxation, and social gatherings.
Anyone who knows me knows I love my glass of red wine. However, while moderate alcohol consumption can be part of a balanced lifestyle, excessive drinking poses significant risks to your health, particularly the affects of alcohol on gut health.
My motto is no judgement and realistic goals.
Understanding how alcohol affects you in various ways can help you make informed choices about your drinking habits. This blog focus on the affect of alcohol on GUT health. To see how else alcohol affects you go to my blog on a comprehensive guide to how alcohol affects you.
The Gut Microbiome: A Delicate Ecosystem
Your gut is home to trillions of microorganisms, including bacteria, fungi, and viruses, collectively known as the gut microbiome. This complex ecosystem plays a crucial role in digestion, nutrient absorption, immune function, and even mental health. Maintaining a balanced microbiome is essential for overall health and well-being.
Disruptions caused by Alcohol on Gut Health Microbiome
-
- Microbial Imbalance (Dysbiosis):
Alcohol consumption can lead to an imbalance in the gut microbiome, known as dysbiosis. Studies have shown that alcohol disrupts the diversity and composition of gut bacteria. Beneficial bacteria, such as Bifidobacteria and Lactobacilli, can decrease, while harmful bacteria, like Proteobacteria, can proliferate. This imbalance can lead to various gastrointestinal issues and systemic health problems.
- Microbial Imbalance (Dysbiosis):
-
- Increased Permeability (Leaky Gut):
Alcohol can damage the lining of the gut, increasing intestinal permeability, commonly referred to as “leaky gut.” When the gut barrier is compromised, toxins, undigested food particles, and harmful bacteria can enter the bloodstream, triggering inflammation and contributing to a range of health issues, including autoimmune diseases, allergies, and chronic inflammation.
- Increased Permeability (Leaky Gut):
-
- Inflammation and Immune Response:
Chronic alcohol consumption can cause inflammation in the gut. Alcohol-induced dysbiosis and leaky gut can activate the immune system, leading to the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines. This persistent inflammation can harm not only the gut but also other organs, potentially leading to liver disease, cardiovascular problems, and even mental health disorders.
- Inflammation and Immune Response:
Effects of alcohol on Digestive Health
-
- Nutrient Absorption:
Alcohol interferes with the absorption of essential nutrients, including vitamins and minerals like B vitamins, vitamin K, folic acid, and iron. Poor nutrient absorption can lead to deficiencies and related health problems, such as anemia, fatigue, and impaired cognitive function.
- Nutrient Absorption:
-
- Gastrointestinal
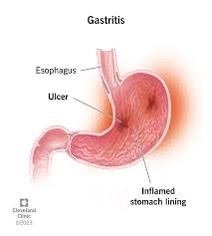 Disorders:
Disorders:
Excessive alcohol consumption is linked to various gastrointestinal disorders, including gastritis, acid reflux, and peptic ulcers. It can also exacerbate symptoms of existing conditions like irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) and inflammatory bowel disease (IBD).
- Gastrointestinal
Mental Health Connection
The gut-brain axis is a bidirectional communication system between the gut and the brain. A healthy gut microbiome produces neurotransmitters like serotonin, which regulate mood and stress responses. Alcohol-induced gut dysbiosis can disrupt this communication, potentially leading to mood disorders such as anxiety and depression.
Practical Tips for Protecting Your Gut Health
-
- Moderate Your Alcohol Intake:
Limit alcohol consumption to moderate levels. For women, this means up to one drink per day, and for men, up to two drinks per day. Avoid binge drinking and try to have alcohol-free days each week.
- Moderate Your Alcohol Intake:
-
- Support Your Gut Microbiome:
Incorporate probiotic-rich foods like yogurt, kefir, sauerkraut, and kombucha into your diet. Prebiotic foods like garlic, onions, bananas, and asparagus can also help nourish beneficial gut bacteria.
- Support Your Gut Microbiome:
-
- Stay Hydrated:
Alcohol is dehydrating, so it’s essential to drink plenty of water to support digestion and overall health.
- Stay Hydrated:
-
- Eat a Balanced Diet:
A diet rich in fibre, fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains can promote a healthy gut. Avoid processed foods and excessive sugar, which can further disrupt the microbiome.
- Eat a Balanced Diet:
-
- Manage Stress:
Chronic stress can negatively impact gut health. Engage in stress-reducing activities such as yoga, meditation, and regular exercise.
- Manage Stress:
Take Charge of Your Gut Health Today!
Understanding the impact of alcohol on your gut health is the first step towards making positive changes. If you’re experiencing digestive issues, nutrient deficiencies, or other health concerns, it’s time to take action. Consulting with a naturopath and nutritionist can provide you with personalised guidance and support tailored to your unique needs.
Schedule a consultation today and discover:
-
- Customised dietary plans to support a healthy gut microbiome.
-
- Natural remedies to heal and protect your gut lining.
-
- Holistic strategies to reduce inflammation and boost nutrient absorption.
-
- Expert advice on managing stress and making sustainable lifestyle changes.
Your journey to optimal health starts here. Don’t wait—reach out to a naturopath and nutritionist now to reclaim your gut health and enhance your overall well-being.
Contact us today to book your appointment and start feeling better naturall
